 Cervus nippon
Cervus nippon
-------------
English: Sika deer
German: Hirsch Sika
France: Sika
Spanish: Sika
Distribution areas
------------------
The sika deer originated in the South-
-Eastern Asiatic territories. Later it was
reared in other localities, especially in
Europe, where conditions were favourable.
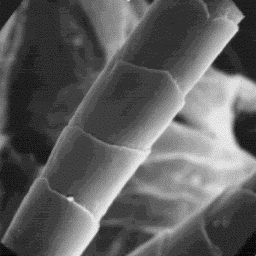
Description of the fur
---------------------- The surface structure
The skins of the sika are from 120 to of the skin, 200x
160 cm long. The coat is thick, containing
coarse and easily breakable fibres especially in the winter season. Long
coarse fibres predominate and are moderately curled along the length. The
fine fur fibres are lightly coloured, short and relatively scarce. These fine
fibres are curled and distinctly bent. The upper part of the coat is grey or
brown-grey in colour. The under fur layer is very short, about 3 to 10 mm.
The coat consists of 40 to 80 mm long guard hair fibres.
|
|
 Cervus nippon
Cervus nippon
-------------
English: Sika deer
German: Hirsch Sika
France: Sika
Spanish: Sika
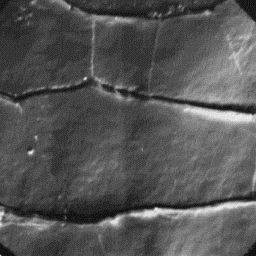
Structure of the hair
---------------------
The microscopic skin surface is usually
smooth; the hair follicles are narrow with
straight edges and contain only one hair
shaft. The summer skin surface structure
appears furrowed.
The fine fur fibres are from 12 to 20 µm The cuticular structure
in diameter. The cross-section is circular of the fine fibres, 2000x
and the cuticular scales are cornet-like
with a smooth surface and straight scale margins. These fine fibres are
non-medullated.
|
|
 Cervus nippon
Cervus nippon
-------------
English: Sika deer
German: Hirsch Sika
France: Sika
Spanish: Sika
The intermediate fibres are present only
in the summer skin. Their diameter is from
30 to 60 µm and the cuticules are of the
even tile-like or crenated tile-like shape.
The cross-section is circular or
ellipsoidal. The scale surface is smooth
and the scale margins are rippled. The
narrow medulla is unbroken and symmetrically
situated in the central axial area of the The cuticular structure
shaft. The overall medullar structure of an intermediate hair, 2000x
belongs to the lattice type. The infilling
medullar substance is of the needle-sheet-like structure.
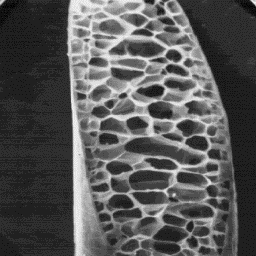
The winter guard hairs are very coarse and easily broken. In the lower
part of the shaft, near to the skin surface, the cross-sectional outline is
circular while, in the middle and upper parts, it is ellipsoidal. The
diameter is in range of 150 to 400 µm. The cuticular scales are even
tile-like, with a smooth surface or, in some cases, the surface is finely
grooved. The scale margins are usually straight.
|
|
 Cervus nippon
Cervus nippon
-------------
English: Sika deer
German: Hirsch Sika
France: Sika
Spanish: Sika
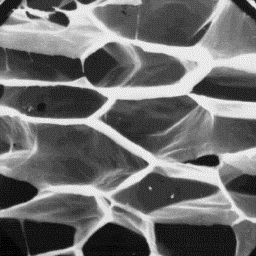
These hairs have a predominating type of
medulla which is unbroken and central
symmetrical-shaped. The overall medullar
structure belongs to the symmetrical non-
-uniform lattice type with larger-sized
cavities distributed on the periphery of the
cross-section. The infilling substance of
the medulla is sheet-like.
Longitudinal section
The summer guard hairs are circular or of a guard hair, 100x
ellipsoidal in cross-section with a diameter
of 60 to 120 µm. The cuticular scales are of the tile-like shape or crenated
tile-like shape. The surface of the scales is smooth and the scale margins
rippled. The medulla is narrow, unbroken and central symmetrical in shape. The
overall medullar structure is of the spongy-lattice type with a complex-sheet
-like infilling substance.
|
|
 Cervus nippon
Cervus nippon
-------------
English: Sika deer
German: Hirsch Sika
France: Sika
Spanish: Sika
Detailed structure
of the medulla, 600x
Numerical code for sika deer skin structure
-------------------------------------------
Surface of the skin: 3-4-1
Fine fur fibres: 1-5-1-1-4-0-0-0-0-12.21-3.15
Intermediate fibres: 1.2-2.4-1-1.2-3-1-1-8-3-30.61-30.65
Guard hairs: 1.2-2.4-1-1.2-3-1-1-5-4-60.121-60.95
|




